WordPress Speed Optimization 2025
What Is WordPress Website Speed Optimization?
A wordpress speed optimization is the process of enhancing a WordPress site’s performance by reducing load times, improving responsiveness, and ensuring visual stability, using techniques like efficient hosting, lightweight themes, caching, image optimization, and code minification. In 2025, with 53% of mobile users abandoning sites that take over three seconds to load, speed is critical for user retention and SEO, directly impacting Google’s Core Web Vitals and search rankings. The benefits of WordPress speed optimization include:
- Improved SEO rankings through better Core Web Vitals scores, such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) under 2.5 seconds.
- Higher conversion rates, with a 1-second speed improvement, potentially boost conversions by 7%.
- Lower bounce rates and keep users engaged for longer.
- Enhanced mobile experience for over 62.5% of global web traffic.
- Reduced server load via caching and CDNs, improving scalability; and 6. Increased customer satisfaction, fostering trust, and repeat visits.
Why Is Speed A Valuable Asset in 2025
For Google, speed is not merely a technical metric; it is the currency of user attention and a cornerstone of business success. Consider this: a one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% loss in conversions, 11% fewer page views, and a 16% decrease in customer satisfaction. For mobile users, the stakes are even higher. Studies consistently show that 53% of mobile visitors will abandon a page if it takes longer than three seconds to load. This isn’t just a statistic; it’s a direct reflection of user behavior in an era of instant gratification.
The landscape has fundamentally shifted. Google’s integration of **Core Web Vitals (CWV)**—a set of user-centric performance metrics—as a confirmed ranking factor has solidified the link between website speed and SEO visibility. A slow website is no longer just a nuisance; it’s a liability that actively harms your search engine rankings, user experience (UX), and ultimately, your conversion rates. As Google’s algorithms become more sophisticated, they increasingly reward websites that provide a seamless, fast, and engaging experience, pushing slower competitors down the search results pages (SERPs).
This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step framework for diagnosing and fixing WordPress site performance issues. Tailored specifically for content-heavy blogs, feature-rich eCommerce stores, and complex enterprise websites, it moves beyond generic advice to offer actionable strategies updated for the technological realities of 2025. We will dissect the foundational elements of speed, from hosting and themes to advanced frontend and backend optimization techniques, equipping you with the knowledge to transform your WordPress site into a high-performance asset that delights users and dominates search results.
Benchmarking Your Speed: The Starting Line
The first principle of performance optimization is unequivocal: you cannot improve what you do not measure. Before implementing any changes, establishing a clear, data-driven baseline is essential. This initial audit provides a snapshot of your site’s current health, identifies the most critical bottlenecks, and allows you to track the tangible impact of your optimization efforts. Without this benchmark, you are navigating blind, unable to distinguish between impactful changes and wasted effort.
Key Tools for Analysis
A robust analysis requires a multi-tool approach, as each offers a unique perspective on performance. While there are dozens of options, three tools form the industry-standard toolkit for a comprehensive speed audit:
- Google PageSpeed Insights (PSI): As Google’s own tool, PSI is indispensable. It provides both “Field Data” from the Chrome User Experience Report (CrUX), which reflects real-world user performance over the last 28 days, and “Lab Data” from Lighthouse for on-demand diagnostics. Its primary value lies in measuring Core Web Vitals and offering actionable recommendations directly from the source.
- GTmetrix: A powerful tool that provides detailed performance reports, including a waterfall chart that visualizes how every asset on your page loads. This is invaluable for identifying specific files—like large images, slow-loading scripts, or external requests—that are creating bottlenecks. It also tracks Core Web Vitals and provides its own performance score.
- WebPageTest: For the most granular analysis, WebPageTest is the tool of choice for advanced developers. It allows you to test from various locations and on different devices and connection speeds, providing a deep dive into every aspect of the loading process, including Time to First Byte (TTFB) and render-blocking resources.
Understanding Key Performance Metrics (KPIs)
Modern performance is measured by a set of user-centric metrics. Understanding these KPIs is crucial for interpreting your test results. Google’s Core Web Vitals are the most critical, as they directly influence SEO rankings.
Core Web Vitals Explained
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. It marks the point when the largest image or text block visible within the viewport is rendered. A fast LCP reassures the user that the page is helpful. Google recommends an LCP of less than 2.5 seconds.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures responsiveness. It assesses the latency of all user interactions (clicks, taps, key presses) made with a page. A low INP means the page feels snappy and responsive to user input. A good INP score is under 200 milliseconds. INP replaced First Input Delay (FID) as a Core Web Vital in 2024.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. It quantifies how much unexpected layout shift occurs as the page loads. A low CLS prevents users from accidentally clicking the wrong element because a button or ad suddenly appears. A good CLS score is less than 0.1.
Beyond the core three, other metrics provide essential diagnostic information:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): Measures server responsiveness. It’s the time between the browser requesting a page and when it receives the first byte of information from the server. A high TTFB points to server-side issues or poor hosting. A TTFB under 800ms is a common target.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): Marks the time when the *first* piece of content from the DOM (e.g., text, image) is rendered on the screen. It’s a key milestone in the user’s perception of loading.
- Total Blocking Time (TBT): A lab-based metric that measures the total time between FCP and Time to Interactive (TTI) where the main thread was blocked long enough to prevent input responsiveness. TBT is a strong proxy for INP.
Actionable Step: Create Your Benchmark Report
To begin your optimization journey, create a simple spreadsheet to record your baseline performance. Test key pages that represent different templates on your site, such as your homepage, a high-traffic blog post, a product page (if applicable), and a category page. This provides a holistic view of your site’s performance.
Use the following table as a template to document your findings. This report will become your single source of truth for tracking progress.
| Page URL | Tool Used | Device | LCP (s) | INP (ms) | CLS | TTFB (ms) | Page Size (MB) | Requests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Your Homepage URL* | PageSpeed Insights | Mobile | ||||||
| *Your Product Page URL* | GTmetrix | Desktop | ||||||
| *Your Blog Post URL* | PageSpeed Insights | Mobile |
With this data in hand, you can now move forward to address the foundational elements that dictate your site’s speed potential.
The Foundation: High-Speed Hosting, Themes, and CDNs
Before a single line of code is minified or an image compressed, your website’s performance is largely predetermined by its foundation. This core infrastructure—comprising your hosting provider, WordPress theme, and Content Delivery Network (CDN)—sets the ceiling for how fast your site can ultimately become. Neglecting this foundation means all subsequent optimization efforts will yield diminishing returns; it’s like trying to win a Formula 1 race in a family sedan. A reliable hosting plan is the first and most critical step.

Choosing a Performance-Optimized Hosting Provider
Your web host is the engine of your website. A slow, poorly configured server will bottleneck your site’s speed regardless of how well-optimized your frontend is. In 2025, the distinction between hosting tiers has become a critical factor in performance.
Managed vs. Shared Hosting: A Crucial Distinction
The type of hosting you choose has a direct and profound impact on speed. While shared hosting is budget-friendly, it comes with significant performance trade-offs.
- Shared Hosting: On a shared plan, your website shares server resources (CPU, RAM) with dozens or even hundreds of other sites. A traffic spike on a neighboring site can slow your site down, a phenomenon known as the “noisy neighbor” effect. These plans offer minimal WordPress-specific optimization.
- Managed WordPress Hosting: This is a premium service where the hosting environment is specifically architected and fine-tuned for WordPress. Providers like WP Engine and Kinsta offer server-level caching, the latest PHP versions, and expert support, which are crucial for high-performance sites. As one expert notes, “Managed WordPress hosting is more like living in a condo… You get a specialized environment optimized specifically for WordPress.”.
Key Hosting Features for Speed in 2025
When evaluating hosting providers, prioritize these technical features:
- Latest PHP Version: Ensure the host supports PHP 8.0 or newer. Each PHP version brings significant performance improvements. An old PHP version can slow down a site by 10-400%.
- Server-Level Caching: This is far more efficient than plugin-based caching. Look for hosts using NGINX as a reverse proxy or those with proprietary caching solutions like WP Engine’s EverCache® or SiteGround’s SuperCacher.
- NVMe Storage: Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) SSDs offer significantly faster read/write speeds than traditional SSDs, leading to quicker database queries and file access.
- Included CDN: Many top-tier hosts now bundle a premium CDN service (like Cloudflare Enterprise) with their plans, simplifying setup and enhancing global performance.
- Server Location: Choose a host with data centers geographically close to your primary audience to reduce latency and TTFB.
Top-performing hosts mentioned across multiple 2025 reviews include WP Engine for enterprise-grade performance, Kinsta for its resource-intensive application handling, Rocket.net for its focus on speed and security, and Securityostinger as a strong value option with LiteSpeed servers.
Selecting a Lightweight and Fast WordPress Theme
Your WordPress theme is the architectural blueprint of your site’s frontend. A bloated theme, laden with excessive JavaScript, poorly optimized CSS, and unnecessary features, is one of the most common causes of a slow website. As Google’s John Mueller stated, a theme impacts everything from headings and text to page load times and structured data.
How to Test a Theme for Speed
Before committing to a theme, conduct due diligence. The most effective method is to test the theme’s *demo site* using Google PageSpeed Insights. This gives you a realistic preview of its out-of-the-box performance. A theme that scores poorly on its own demo is a major red flag.
Characteristics of a Fast Theme
- Lightweight Codebase: A fast theme should have a small file size. For example, GeneratePress boasts an install size of less than 10KB.
- Minimal Dependencies: Modern, fast themes often avoid relying on heavy libraries like jQuery, which can be render-blocking.
- Clean, Semantic HTML: A well-coded theme uses proper HTML5 tags (“, “, “), which helps search engines understand your content structure and avoids “div soup” that can confuse crawlers.
- Optimized for Core Web Vitals: The best themes are built with LCP, INP, and CLS in mind, ensuring responsive design and visual stability.
- Selective Feature Loading: Look for themes that only load scripts for features you are actively using, rather than loading all assets on every page.
Recommended Fast Themes for 2025
Based on numerous performance tests and expert reviews from 2025, a few themes consistently rise to the top for their speed and efficiency.
| Theme | Type | Best For | Key Performance Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Astra | Lightweight & Multipurpose | All-around use, beginners | Ranked as one of the fastest lightweight themes with a 2.1s load time in tests. |
| GeneratePress | Lightweight & Developer-Friendly | Developers, performance purists | Excellent mobile and desktop PSI scores, clean code. |
| Kadence | Feature-Rich & Lightweight | Users wanting features without bloat | Modular design only loads scripts for activated features. |
| Neve | Mobile-First & Fast | Mobile-heavy traffic sites | Achieved a perfect 100 score in PageSpeed Insights tests. |
| Divi | Page Builder-Centric | Visual designers, agencies | Built-in performance optimization tools and a powerful visual builder. |
| Hello Elementor | Barebones Starter | Elementor users building from scratch | Extremely lightweight (6KB), as it’s a blank canvas for the builder. |
Implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
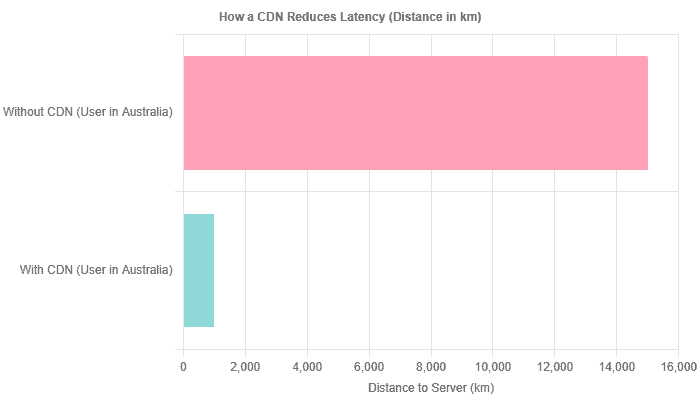
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a non-negotiable component of a modern performance strategy, especially for sites with a global audience. It dramatically reduces latency by caching your site’s static assets—images, CSS, and JavaScript—on a distributed network of servers worldwide.
What a CDN Is and Why It’s Essential
When a user visits your site, their request travels to your origin server. If that user is in Australia and your server is in New York, the physical distance creates a delay (latency). A CDN solves this by serving a cached copy of your site from a server (or “Point of Presence” – PoP) much closer to the user, for example, in Sydney. This simple change can reduce page load times by up to 44% or more.
How to Set It Up
Setting up a CDN is easier than ever. Many top hosts include it, but if yours doesn’t, here are the best options:
- Cloudflare: The most popular choice, offering a generous free plan that includes a global CDN and robust DDoS protection. Setup is as simple as changing your domain’s nameservers. We use Cloudflare on WPBeginner for its security and performance benefits.
- Bunny.net: A highly-regarded premium CDN known for its excellent performance and affordable pay-as-you-go pricing. It’s a favorite among performance-conscious developers and is praised for its easy-to-use WordPress plugin.
- Plugin Integration: Caching plugins like WP Rocket offer dedicated tabs to easily integrate your chosen CDN, rewriting your asset URLs automatically.
Core Frontend Optimization Techniques
With a solid foundation in place, the next layer of optimization focuses on the frontend—the elements that a user’s browser must download and render to display your page. These techniques are among the most impactful for improving Core Web Vitals and perceived performance, as they directly address the size and delivery of your site’s assets.
Mastering Image Optimization
Images are frequently the single most significant contributor to page weight. According to HTTP Archive, media files can account for over two-thirds of a page’s total data. Unoptimized images are a primary cause of slow load times and poor LCP scores. A comprehensive image optimization strategy is therefore not optional; it’s essential.
1. Resize Images Before Uploading
The most fundamental step is to resize images to the exact dimensions they will be displayed at on your site. Uploading a 4000px-wide photo for an 800px-wide blog content area forces the user to download a file that is unnecessarily large, which the browser then has to scale down. Use an image editor like Photoshop or free online tools to resize images to their final display size *before* uploading them to the WordPress Media Library.
2. Compress Images to Reduce File Size
Compression reduces an image’s file size by removing redundant data. There are two main types:
- Lossy Compression: Significantly reduces file size by permanently removing some data. While there is a minor quality reduction, it is often imperceptible to the human eye and is the recommended method for most web use.
- Lossless Compression: Reduces file size without any loss of quality by compressing data non-destructively. The file size reduction is smaller than with lossy compression.
3. Use Next-Gen Image Formats
Modern image formats offer superior compression and quality compared to older formats like JPEG and PNG. In 2025, you should prioritize:
- WebP: Offers both lossy and lossless compression and is widely supported by all modern browsers. It can reduce file sizes significantly compared to JPEG and PNG.
- AVIF: An even newer format that provides superior compression to WebP, resulting in even smaller file sizes. Browser support is growing rapidly.
Many image optimization plugins can automatically convert your uploaded images to these formats and serve them to compatible browsers.
4. Implement Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is a technique that defers the loading of off-screen images and iframes until the user scrolls down to them. This dramatically improves the initial page load time and LCP score because the browser doesn’t have to download every image on the page at once. Since WordPress 5.5, native lazy loading is enabled by default using the `loading=” lazy”` attribute, but plugins can offer more advanced control. Lazy loading is a cornerstone of modern web performance.
Tools & WordPress Plugins for Image Optimization
Manually optimizing every image is tedious. WordPress plugins can automate this entire workflow.
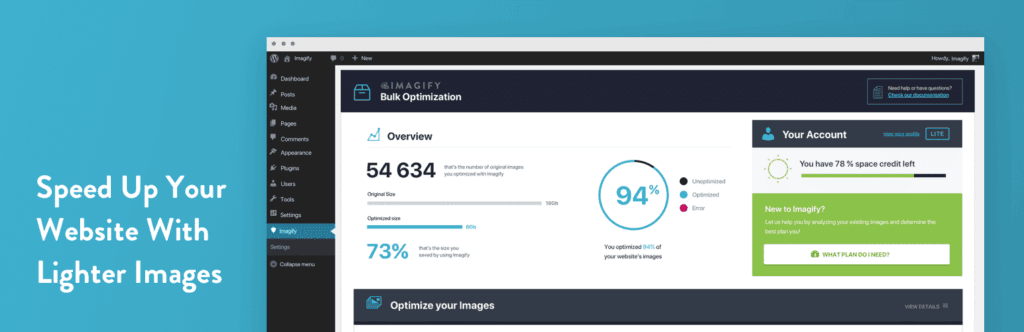
The Imagify plugin offers multiple compression levels, including a “Smart” mode that automatically balances quality and file size.
The Imagify plugin offers multiple compression levels, including a “Smart” mode that automatically balances quality and file size.
- Imagify: Developed by the team behind WP Rocket, Imagify is a user-friendly plugin that offers three compression levels (Normal, Aggressive, Ultra) and automatically converts images to WebP. Its “Smart Compression” mode is particularly effective at finding the optimal balance between size and quality.
- ShortPixel: A highly popular and feature-rich plugin that supports lossy, glossy, and lossless compression. It also offers PDF optimization and can convert images to both WebP and AVIF formats.
- EWWW Image Optimizer: A versatile option that can perform optimizations on your own server (for free, with limitations) or via their premium cloud-based service for more powerful compression.
Minifying and Combining Code (CSS & JavaScript)
Your theme and plugins load CSS and JavaScript files to control your site’s appearance and functionality. Often, these files contain unnecessary characters like whitespace, comments, and line breaks, which increase their size. Furthermore, a site may load dozens of separate files, each requiring an individual HTTP request, which adds overhead and slows down rendering.
- Minification: This process removes all non-essential characters from code files, reducing their size without altering their function.
- Combination (or Concatenation): This technique combines multiple CSS or JavaScript files into a single file, reducing the number of HTTP requests the browser needs to make.
While this sounds technical, leading performance plugins automate this process. Plugins like WP Rocket and Autoptimize allow you to enable minification and combination with a single click in their settings panels. However, it’s crucial to test your site thoroughly after enabling these features, as they can sometimes cause conflicts with specific themes or plugins.
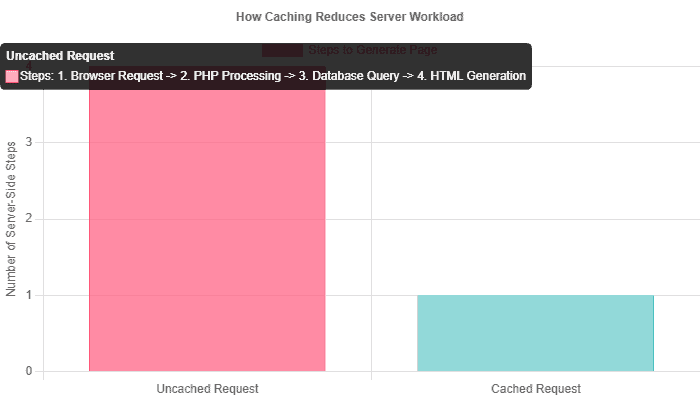
Implementing a Robust Caching Strategy
By default, WordPress is a dynamic CMS. Each time a user visits a page, WordPress queries the database and uses PHP to assemble the page on the fly. This process is resource-intensive and slow. Caching dramatically speeds this up by creating and storing a static HTML version of your pages.
Types of Caching
- Page Caching: This is the most impactful type. It serves a pre-built static HTML page to visitors, bypassing the slow PHP and database processing. This is the primary function of plugins like WP Rocket.
- Browser Caching: This instructs a visitor’s browser to store static files (like your logo, CSS, and JS) locally on their device. When they visit another page on your site, these files are loaded from their local cache instead of being re-downloaded, speeding up subsequent page views.
- Object Caching: A more advanced technique that stores the results of common database queries. It’s particularly effective for dynamic sites like WooCommerce stores or membership sites. This is often handled at the server level by managed hosts using systems like Redis or Memcached.
Choosing the Right Caching Plugin
A good caching plugin is the single most effective tool for improving WordPress speed. Here are the top choices for 2025:
WP Rocket: Widely regarded as the best all-in-one premium caching plugin. It’s incredibly beginner-friendly, applying 80% of performance best practices upon activation. It handles page caching, browser caching, GZIP compression, and integrates file optimization features seamlessly. WPBeginner recommends WP Rocket as the best overall performance plugin.
W3 Total Cache: A powerful and highly configurable free plugin. It offers a vast array of settings, including various caching methods (page, object, database) and CDN integration. Its complexity makes it better suited for advanced users who need granular control.
LiteSpeed Cache: An exceptional free plugin that offers server-level caching, but with a significant caveat: it only delivers its full potential on servers running LiteSpeed Web Server, which is familiar with hosts like Hostinger but not with all providers.
Advanced Performance Tuning
Once you’ve mastered the frontend fundamentals, you can unlock further speed gains by diving into advanced optimization techniques. These methods address more complex bottlenecks within your site’s database and rendering process. While more technical, they can provide a significant competitive edge, especially for dynamic and feature-rich websites.
Deep-Dive into Database Optimization
Your WordPress database is the central repository for all your content, settings, and user data. Over time, it can become bloated with unnecessary information, causing queries to slow down and increasing server response times (TTFB). A clean, efficient database is critical for a fast backend and a snappy user experience.
Common Causes of Database Bloat
- Post Revisions: WordPress automatically saves multiple versions of your posts and pages. While useful, this can lead to hundreds of unnecessary rows in your `wp_posts` table.
- Spam and Unapproved Comments: If not regularly cleaned, spam comments can clutter your `wp_comments` table.
- Transients: These are temporary cached data stored in the `wp_options` table. Sometimes, plugins fail to remove expired transients, leading to bloat.
- Orphaned Data: Data left behind by uninstalled plugins or themes can accumulate over time.
Actionable Steps for Database Cleanup
- Backup Your Database: Before making any changes, always create a complete backup of your database. A mistake here can be catastrophic. Use a plugin like UpdraftPlus or your host’s backup tool.
- Limit Post Revisions: You can limit the number of revisions stored by adding a line of code to your `wp-config.php` file: `define( ‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’, 3 );`. This limits revisions to the three most recent.
- Use a Database Optimization Plugin: For most users, a plugin is the safest and easiest way to clean the database. WP-Optimize is a popular free plugin that can clean post revisions, spam comments, transients, and perform table optimization with a few clicks. WP Rocket also includes a database optimization tab with similar features.
- Optimize Tables via phpMyAdmin (Advanced): For users comfortable with direct database management, you can use a tool like phpMyAdmin (usually provided by your host) to select your database tables and run the `OPTIMIZE TABLE` command. This defragments the tables and reclaims unused space, similar to optimizing a hard drive.
Deferring and Delaying JavaScript
Modern websites are heavily reliant on JavaScript for interactivity, analytics, and third-party features. However, JavaScript is “render-blocking” by default. This means the browser must pause rendering the page to download, parse, and execute JS files as it encounters them, which can severely delay FCP and LCP.
The Solution: Defer and Delay
- Deferring JavaScript: By adding the `defer` attribute to a script tag, you tell the browser to download the script in the background while it continues to parse the HTML. The script is only executed after the HTML document has been fully parsed. This is ideal for scripts that are not needed for the initial render.
- Delaying JavaScript Execution: This is a more aggressive technique that delays the loading and execution of scripts (especially third-party ones like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or chat widgets) until the first user interaction (e.g., a scroll, click, or mouse movement). This can provide a massive boost to initial load times and Core Web Vitals scores.
Implementing this manually is complex, but performance plugins make it simple. WP Rocket provides simple checkboxes for “Load JavaScript deferred” and “Delay JavaScript execution”, allowing you to easily apply these powerful optimizations.
Generating and Inlining Critical CSS
Similar to JavaScript, CSS files are also render-blocking. The browser must download and parse all CSS files before it can render any part of the page, which can lead to a blank white screen for several seconds on slow connections. The solution is to optimize the “Critical Rendering Path.”
The Concept of Critical CSS
Critical CSS is the absolute minimum set of styles required to render the visible, above-the-fold portion of the page. The strategy involves:
- Identifying and Extracting the essential CSS for a given page.
- Inlining this critical CSS directly into the “ section of the HTML document. This allows the browser to render the top part of the page almost instantly, without waiting for an external stylesheet to download.
- Loading the Full CSS File Asynchronously (non-render-blocking) so that it doesn’t hold up the initial page render.
This technique dramatically improves perceived performance and scores for FCP and LCP. While manually generating critical CSS is a complex task for developers, plugins like WP Rocket and platforms like NitroPack have automated this process. They can generate unique, essential CSS for each page on your site, providing a significant performance boost with minimal effort.
Specialized Optimization for High-Stakes Websites
While general performance principles apply to all WordPress sites, certain types of websites face unique challenges that require specialized optimization strategies. eCommerce stores, content-heavy blogs, and large enterprise sites each have distinct bottlenecks that can severely impact speed if not addressed correctly.
eCommerce (WooCommerce) Speed Optimization
WooCommerce sites are inherently dynamic and resource-intensive. The complexity of managing products, inventory, user accounts, and payment gateways creates significant performance hurdles.
The Core Challenges
- Uncachable Pages: Key pages like Cart, My Account, and Checkout are unique to each user and cannot be served from a page cache. These pages must be generated dynamically for every visit, putting a direct strain on the server.
- Database Bottlenecks: A large number of products, variations, and orders leads to massive database tables. Complex queries for filtering products or retrieving order history can be slow and CPU-intensive.
- Plugin Bloat: eCommerce sites often rely on numerous plugins for payments, shipping, and marketing, each adding its own scripts and database queries, which can lead to conflicts and slowdowns.
Solutions for a Faster WooCommerce Store
- High-Performance Hosting with Object Caching: This is non-negotiable for serious eCommerce. A managed host with server-level caching and an object cache (like Redis) can dramatically speed up the processing of dynamic, uncachable pages by caching database queries. Object caching can reduce database load by up to 95%.
- Smart Caching Plugin Configuration: Use a caching plugin that is “WooCommerce-aware.” For example, WP Rocket automatically excludes cart and checkout pages from the cache to prevent functionality issues, ensuring a smooth purchasing process.
- Bulk Image Optimization: Product galleries can contain hundreds of images. Use a plugin like Imagify or ShortPixel to bulk-optimize your entire media library and ensure all product images are compressed and served in next-gen formats.
- Streamline Plugins: Regularly audit your plugins. Disable or remove any that are not essential to the core shopping experience. Too many plugins can slow down both the frontend and the backend admin area.
The impact of these optimizations is direct and measurable. A case study by Deloitte found that a 0.1-second improvement in loading speed increased conversions for retail brands by 8.4%. For an e-commerce store, speed is directly tied to revenue.
Content-Heavy Sites (Blogs, News, Magazines)
Blogs and online magazines thrive on a large volume of content, but this can lead to performance degradation over time as the database grows and archives become unwieldy.
The Core Challenges
- Extensive Database: Thousands of posts, comments, and post metadata can bloat the database, slowing down query times.
- Image-Heavy Content: Articles often feature numerous images, which can significantly increase page weight and load times if not optimized.
– **Slow Archive Pages:** Category and tag archives can become very slow to load if they display full posts instead of excerpts.
Solutions for Fast Content Sites
- Implement Comment Pagination: If your posts receive many comments, they can slow down page load. In WordPress, navigate to `Settings > Discussion` and enable the “Break comments into pages” option. This splits comments into manageable, paginated sections.
- Use Excerpts on Archives: Instead of showing the full content of each post on your blog’s homepage and archive pages, display excerpts. This can be set under `Settings > Reading` by selecting “Excerpt” for the “For each post in a feed, include” option. This dramatically reduces the amount of data that needs to be loaded on these pages.
- Leverage a CDN: A CDN is crucial for content-heavy sites to offload the delivery of images and other static assets, reducing the strain on your origin server and speeding up load times for a global audience.
- Regular Database Maintenance: Schedule regular database cleanups using a plugin like WP-Optimize to remove old post revisions, spam comments, and other unnecessary data.
Enterprise & Complex Business Sites
Enterprise websites often feature complex functionality, custom integrations, and a large stack of plugins, creating a challenging environment for maintaining performance and security Challenges
- Plugin Conflicts and Bloat: A large number of plugins increases the risk of JavaScript/CSS conflicts and performance degradation. Managing this “plugin stack” is a key challenge.
- Security vs. Performance: Many security plugins, particularly those that run scans on the web server, can consume significant resources and slow down the site.
- Custom Code and Integrations: Custom-coded features or third-party API integrations can introduce performance bottlenecks if not developed with efficiency in mind.
Solutions for Robust Enterprise Sites
- Conduct Regular Plugin Audits: Periodically review every plugin. Ask: Is this plugin still necessary? Is there a more lightweight alternative? Is it well-coded and regularly updated? Deactivating and deleting unnecessary plugins is a significant way to improve performance.
- Curate a Lean “Plugin Stack”: Instead of using many single-function plugins, opt for a few powerful, well-coded, multipurpose plugins. For example, a premium performance plugin like WP Rocket can replace separate plugins for caching, lazy loading, and database optimization.
- Offload SecuritSecurityloud-Based Firewall: To balance securitSecurityrformance, use a DNS-level or cloud-based Web Application Firewall (WAF) like Cloudflare or Sucuri. These services filter malicious traffic before it even reaches your server, offloading the security processing and preventing it from impacting your site’s speed. This is often preferable to server-side scanners like Wordfence, which can be resource-intensive.
- Code Profiling: For sites with custom development, use tools like Query Monitor or New Relic to profile the code and identify slow database queries or inefficient functions that are causing delays.
The Ultimate WordPress Speed Plugin Stack
Navigating the vast ecosystem of WordPress plugins can be overwhelming. While the “less is more” principle is a good starting point, the right combination of high-quality plugins—a well-curated “plugin stack”—is essential for achieving peak performance. This section provides an opinionated guide to the best-in-class plugins for speed optimization, categorized by their primary function.
All-in-One Performance Suites
For most users, an all-in-one performance plugin is the most effective and user-friendly solution. These plugins bundle multiple optimization features into a single, cohesive package, reducing the risk of conflicts and simplifying configuration.
- WP Rocket: Widely considered the gold standard for premium WordPress performance plugins. Its key strength is its simplicity; it applies about 80% of web performance best practices automatically upon activation. It expertly handles page caching, file minification, lazy loading, database optimization, and delaying JavaScript execution, all from a clean, intuitive interface. It’s the top recommendation for most users who want a powerful, easy-to-use solution.
- NitroPack: More than just a plugin, NitroPack is a complete optimization platform. It takes a more aggressive, automated approach, running optimizations on its own servers and serving content via its built-in CDN. While it can produce dramatic speed improvements, especially for sites heavy with page builders, its “all-or-nothing” approach offers less granular control than WP Rocket. It’s an excellent choice for those who want a hands-off, maximum-impact solution.
Specialized Optimization Plugins
In some cases, you may want to supplement an all-in-one suite or build your own stack using specialized plugins. This approach offers more granular control but requires more technical knowledge to avoid conflicts.
| Category | Recommended Plugin | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caching | W3 Total Cache | Advanced users on a budget | Offers extensive configuration options, including object and database caching. |
| LiteSpeed Cache | Users on LiteSpeed servers | Powerful server-level caching that outperforms plugin-based methods. | |
| Image Optimization | Imagify | Ease of use and quality | Smart Compression mode and seamless integration with WP Rocket. |
| ShortPixel | Feature set and format support | Supports both WebP and AVIF formats, plus PDF optimization. | |
| Asset Optimization | Perfmatters | Granular script management | Allows disabling of scripts on a per-page/post basis to reduce bloat. |
| Autoptimize | Free and effective code minification | Focuses solely on aggregating and minifying CSS and JavaScript files. | |
| Database Cleanup | WP-Optimize | All-in-one database maintenance | Cleans revisions, transients, and spam, and optimizes database tables. |
Troubleshooting Common Performance Issues
Even with a well-optimized site, performance issues can arise, often due to plugin conflicts, theme changes, or backend bottlenecks. This section provides a practical framework for diagnosing and resolving the most common WordPress speed problems.
Identifying Conflicting Plugins
A frequent cause of a slow or broken site is a conflict between plugins or between a plugin and your theme. This often occurs after an update.
The Standard Troubleshooting Method
The classic method for identifying a problematic plugin is systematic deactivation. While time-consuming, it is highly effective.
- Create a Backup: Before you begin, always back up your website.
- Clear All Caches: Purge your server, plugin, and browser caches to ensure you’re seeing the latest version of your site.
- Deactivate All Plugins: Go to your WordPress dashboard, select all plugins, and deactivate them in bulk.
- Check the Site: If the issue is resolved, you know a plugin is the culprit.
- Reactivate One by One: Activate each plugin one at a time, checking your site after each activation. When the issue reappears, you have found the conflicting plugin.
According to experts, conflicts most frequently follow batch updates, which is why updating plugins individually and testing after each one is a recommended best practice.
Using Advanced Tools for Diagnosis
For more subtle issues, especially those causing a slow backend, you may need a more advanced tool. Query Monitor is a free developer tool that provides detailed insights into your site’s database queries, hooks, and HTTP requests on a per-page basis. It can help you pinpoint exactly which plugin is running slow queries and causing delays.
What to Do After a Theme Change
Changing your WordPress theme is more than a cosmetic update; it’s a foundational shift that can significantly impact SEO and performance. A new theme can introduce different scripts, change HTML structure, and have different image size requirements.
Common Issues After a Theme Switch
- Loss of Functionality: Features that were built into the old theme, such as sliders or custom post types, will disappear. Theme-specific shortcodes will also break, appearing as plain text in your content.
- Performance Changes: A new theme can be faster or slower than the old one. A bloated, feature-heavy theme can negatively impact your Core Web Vitals.
- Image Display Issues: The new theme will likely have different default image sizes. Previously uploaded featured images and thumbnails may appear stretched or blurry.
Post-Change Checklist
- Re-run Speed Tests: Immediately benchmark your new theme’s performance against your old records to identify any regressions.
- Check for Broken Links and 404s: Ensure the new theme hasn’t altered your URL structure.
- Re-configure Plugin Settings: Some plugin settings, especially those related to performance and display, may need to be adjusted to work correctly with the new theme.
- Regenerate Thumbnails: Use a plugin like Regenerate Thumbnails to resize your existing images to match the new theme’s dimensions.
- Submit a New Sitemap: After a significant structural change, it’s wise to submit your updated XML sitemap to Google Search Console to encourage re-crawling.
A traffic drop of less than 10% after a redesign is often normal and should recover within a few weeks, but monitoring is key to catching deeper issues.
FAQs: Your WordPress Speed Questions Answered
Why is my WordPress website so slow?
A slow WordPress site is typically caused by a combination of factors. The most common culprits are: inadequate web hosting (especially cheap shared hosting), large and unoptimized image files, an excessive number of poorly coded plugins, a bloated theme with unnecessary features, and a lack of caching, which forces your server to rebuild every page for every visitor. External scripts from ads or third-party tools can also significantly impact performance.
How can I speed up my WordPress site for free?
You can achieve significant speed improvements without spending money. Start by implementing a free caching plugin like W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache. Manually compress and resize your images before uploading them. Use Cloudflare’s free plan, which provides a basic CDN and other performance benefits. Regularly clean your database by deleting spam comments and old post revisions. Lastly, ensure your theme and plugins are updated, and remove any you are not using.
Does the number of plugins slow down WordPress?
Yes, but it’s more about the quality and function of the plugins than the sheer number. A single poorly coded plugin can have a more detrimental effect on performance than ten lightweight, well-built ones. Plugins that add a lot of scripts to the frontend, perform complex database queries, or run continuous background processes are familiar sources of slowdowns. It’s a best practice to periodically review and delete plugins you no longer need and choose high-quality, actively maintained plugins.
What is a good page load time for WordPress in 2025?
In 2025, a good page load time is generally considered to be under 2 seconds. However, user expectations are constantly increasing. Studies show that 47% of people expect a site to load in under 2 seconds, and conversion rates are significantly higher for sites that load in 1 second or less. For Google’s Core Web Vitals, a Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) score of under 2.5 seconds is required to be in the “Good” category.
How do I fix a slow WordPress admin dashboard?
A slow `wp-admin` dashboard is almost always a server-side issue. The most common causes are a bloated database, a resource-heavy plugin, or an outdated PHP version. To fix this, start by performing a database cleanup using a plugin like WP-Optimize. Then, use a diagnostic plugin like Query Monitor to identify if a specific plugin is making slow database queries. Finally, check with your hosting provider to ensure you are running a recent version of PHP (ideally 8.0 or higher) and that your hosting plan has sufficient resources (RAM and CPU) for your site’s needs.
Conclusion: Speed is a Journey, Not a Destination
Optimizing a WordPress website for speed in 2025 is a multifaceted discipline that extends far beyond installing a single plugin. It is a continuous process of measurement, refinement, and adaptation. As we’ve explored, actual performance is built upon a solid foundation, layered with meticulous frontend optimizations, and fine-tuned with advanced backend techniques. The digital landscape is unforgiving to the slow; user expectations are higher than ever, and search engines like Google explicitly reward sites that deliver a fast, seamless experience.
The journey to a faster website begins with a few critical, high-impact actions. By prioritizing these steps, you can achieve the most significant gains with the least initial effort:
- Invest in Quality Hosting: Your hosting provider sets the upper limit of your site’s potential speed. A managed WordPress host with server-level caching and modern infrastructure is the single most important investment you can make.
- Choose a Lightweight Theme: A bloated theme will sabotage your efforts from the start. Select a well-coded, performance-focused theme and test it before committing.
- Implement a CDN: A Content Delivery Network is essential for serving a global audience quickly and reducing the load on your origin server. Cloudflare’s free plan is an excellent starting point for any site.
- Use a High-Quality Caching Plugin: A plugin like WP Rocket is the cornerstone of WordPress performance, automating complex tasks like page caching, file minification, and script deferral.
- Master Image Optimization: Images are often the heaviest assets on a page. A disciplined workflow of resizing, compressing, and using next-gen formats is non-negotiable.
Remember that speed optimization is not a one-time fix but an ongoing commitment to providing the best possible user experience. Regularly benchmark your site, stay informed about evolving best practices, and be prepared to adapt as new technologies and algorithms emerge. By treating performance as a core pillar of your digital strategy, you not only improve your chances of ranking higher but also build a more resilient, engaging, and profitable online presence.
Harnessing actual WordPress performance requires a holistic, multi-layered approach to speed optimization, moving far beyond simple installs. The journey to a fast WordPress site begins with the foundation: choosing managed WordPress hosting like WP Engine over volatile shared hosting to secure the most optimized server configurations with an ideal PHP version and sufficient server resources.
This foundational strength, coupled with a powerful caching plugin like WP Rocket for browser caching and gzip compression, is key to drastically improving website performance and reducing server load. For the frontend, achieving a high Google Page Speed Score in Google PageSpeed Insights and addressing Core Web Vitals requires rigorous image optimization (using image compression tools like WP Optimize and lazy loading to optimize images in your WordPress media library), and managing CSS and JavaScript files to eliminate render blocking resources.
By minimizing external HTTP requests from external scripts, utilizing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve static resources, and cleaning up the WordPress database from bloat caused by installed plugins and intensive database queries, you ensure your WordPress website can load faster. Ultimately, every element, from the minimal footprint of your chosen WordPress theme to configuring optimal WordPress settings and auditing the impact of too many plugins, contributes to a final website speed that meets the standards of a crucial ranking factor, transforming your WordPress site from a slow website to a speed champion in every speed test.
Start today. Benchmark your site, identify your biggest bottleneck, and tackle one optimization at a time. The rewards—in the form of better rankings, higher conversions, and a superior user experience—are well worth the effort.

With over 27 years of hands-on SEO expertise, starting from my early days as a CFO. Quitting that job to build a top-ranked web hosting business in 1995, I’ve mastered WordPress optimization as a precise engineering discipline. Through extensive research, high-level consulting, and developing a WordPress site that achieved over a thousand organic Google rankings—culminating in a six-figure sale—I’ve decoded Google’s algorithm over 27 years to develop wordpress engineering that transforms underperforming WordPress sites into authoritative powerhouses. Business owners frustrated by stagnant traffic, low visibility, and missed opportunities find relief as I help them deliver measurable ROI through higher rankings, increased leads, and sustainable growth. As owner of dominant city-based SEO platforms in major U.S. markets, I outperform industry gurus, empowering entrepreneurs, local businesses, agencies, and marketers via my WordPress Optimization services at wordpressoptimization.com to unlock their site’s full potential.