Mastering PHP 8/8.x for WordPress: 2025 Guide to Performance, Upgrade Checklist
TL;DR: Upgrading WordPress sites to PHP 8.x offers significant benefits in speed, efficiency, security, and SEO. Sites currently running on versions like PHP 7.4 or earlier face increasing risk and performance penalties. The guide provides a structured, three-phase roadmap—pre-flight preparation (backup, compatibility checking), execution (staging environment, debugging, testing), and post-launch validation—to ensure the upgrade is smooth and low-risk. It also covers advanced tuning options (OPcache, JIT, object caching) to further optimize performance. For most sites, switching to PHP 8.3 is recommended, with PHP 8.2 as a stable fallback if compatibilities demand it.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Your Website is Slower Than It Should Be
- Part 1: The “Why” – Quantifying the Gains of a PHP 8.x Upgrade
- Part 2: The “How-To”: Your Bulletproof PHP 8.x Upgrade Roadmap
- Part 3: Advanced Tuning — Squeezing Out Every Drop of Performance
- Conclusion & Your Next Steps
- Frequently Asked Questions (For “People Also Ask”)
What is PHP 8/8.x and WordPress?
Upgrading your WordPress site to PHP 8.3 or higher is no longer optional—it’s essential. As of mid-2025, over 42% of WordPress sites still run on outdated PHP versions, exposing them to security vulnerabilities and performance bottlenecks. In contrast, PHP 8.x introduces significant improvements in speed, efficiency, and SEO, transforming your site into a more secure and user-friendly experience.
However, to fully leverage these benefits, choosing the right WordPress hosting provider is crucial. A high-performance host ensures that your site can handle the increased demands of modern PHP while providing the necessary support for a smooth upgrade.
Key Benefits of Choosing the Best WordPress Hosting Providers for Performance and Support
-
Optimized Server Configuration: Top hosts offer PHP 8.x compatibility and advanced caching mechanisms, ensuring your site runs efficiently.
-
Enhanced Security Measures: Leading providers implement robust security protocols, safeguarding your site against potential threats.
-
Expert Technical Support: Access to knowledgeable support teams can help resolve issues promptly, minimizing downtime.
-
Scalability Options: Reputable hosts provide scalable solutions to accommodate your site’s growth without compromising performance.
-
Regular Software Updates: Reliable hosts ensure timely updates to PHP and other critical software, keeping your site secure and up-to-date.
By selecting a hosting provider that aligns with these criteria, you can maximize the advantages of PHP 8.x, leading to a faster, more secure, and more efficient WordPress site.
Your Website is Slower Than It Should Be
Imagine this: a client’s WooCommerce shop, which had been performing adequately but not exceptionally on PHP 7.4, was experiencing a slow creep in bounce rates. After a focused, 15-minute session to upgrade the site to PHP 8.3 and adjust a few server settings, the page load time plummeted from 4.2 seconds to just under two. The result? A nearly 25% increase in sales the following month. This isn’t a magical anecdote; it’s a real-world case study demonstrating the untapped power of modern PHP that a vast majority of WordPress sites are leaving on the table.
As of mid-2025, a startling portion of the web, which is over 42% powered by WordPress, continues to operate on outdated and unsupported versions of PHP. PHP is the server-side scripting language that acts as the engine for every WordPress site. Running on an old version like PHP 7.4, whose official security support ended in November 2022, is akin to driving a high-performance car with worn-out brakes and an inefficient engine. It exposes your digital presence to significant security vulnerabilities, sluggish performance, and a frustrating user experience—all factors that directly harm your search engine rankings.
The hesitation to upgrade is understandable. Forum posts and Reddit threads are filled with stories of sites breaking, plugins failing, and the dreaded “white screen of death.” But these issues are almost always preventable. They stem not from the upgrade itself, but from a lack of a methodical, test-driven process.
This guide is your definitive, step-by-step roadmap to safely and effectively upgrading your WordPress site to PHP 8.x. We will cut through the technical jargon and online noise to provide a clear, actionable plan grounded in extensive benchmark data and real-world best practices. We will cover the “why”—the quantifiable performance, efficiency, and SEO gains that make this upgrade a strategic necessity—and the “how”—a bulletproof checklist to ensure a smooth, successful transition. By the end of this document, you will not only understand the imperative to upgrade but will be fully equipped to execute it with confidence.
Part 1: The “Why” – Quantifying the Gains of a PHP 8.x Upgrade
Before diving into the technical process, it’s crucial to understand the tangible benefits of upgrading. This isn’t just about keeping software current; it’s about unlocking a new level of performance, efficiency, and security that directly impacts your bottom line. We’ll explore this through three core pillars: raw performance, server efficiency, and the undeniable impact on SEO.
1.1 Raw Performance Boost: Faster Than Ever
The most immediate and noticeable benefit of moving to a modern PHP version is a significant increase in speed. This is measured by how many requests per second (req/s) a server can handle. More requests per second means your site can serve more visitors simultaneously without slowing down, and individual pages load faster for each user.
Analysis of Benchmark Data
Multiple independent benchmarks consistently demonstrate this performance leap. Let’s analyze two key studies:
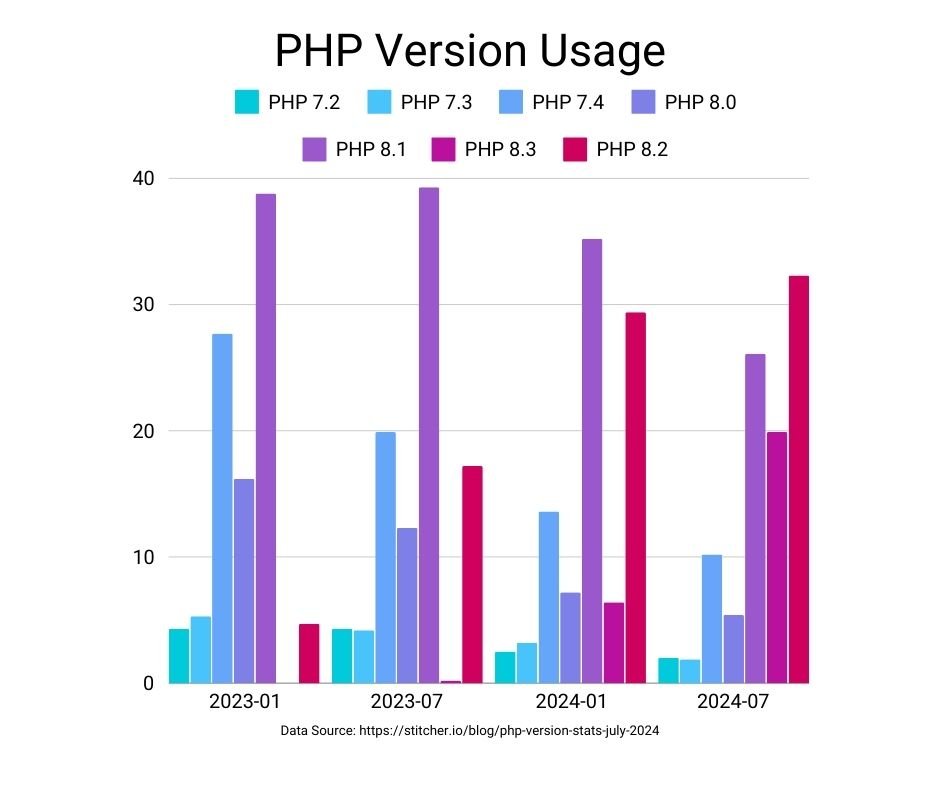
Kinsta’s 2024 Benchmark: A comprehensive test conducted by hosting provider Kinsta provides a clear picture of the performance progression. Using WordPress 6.4.2, their results show a steady improvement with each successive PHP version. Upgrading from PHP 7.4 to PHP 8.3 resulted in a 13.4% increase in throughput, from 149 req/s to 169 req/s. For resource-intensive platforms like WooCommerce, the gains are even more pronounced. The same study found that PHP 8.3 could handle nearly 21% more requests per second than PHP 7.4 (58 req/s vs. 48 req/s), a critical advantage for any online store.
Data Source: Kinsta PHP Benchmarks (Dec 2023). Chart shows requests per second (higher is better) for WordPress 6.4.2 and WooCommerce 7.9.0.
Pressidium’s 2025 Benchmark: Another study, this time from Pressidium, introduces a crucial nuance. Their tests, run on WordPress 6.5.5, also showed a massive performance jump from PHP 7.4 to PHP 8.0, with mean response time dropping from 91.7ms to 67.1ms (a 27% improvement). However, they observed a slight performance regression with PHP 8.1 and 8.2 compared to 8.0. PHP 8.1 showed the highest mean processing time in their test suite. This doesn’t invalidate the overall trend but serves as a powerful reminder: “latest” is not always “fastest” in every single environment. Performance can vary based on server hardware, specific site configuration, and the nature of the workload. This underscores the absolute necessity of testing in your own staging environment before committing to a version.
Data Source: Pressidium PHP Performance Tests (Sep 2025). Chart shows mean server processing time in milliseconds (lower is better).
Key Performance Takeaway
Upgrading from PHP 7.4 to a modern 8.x version (specifically 8.0 or 8.3, based on current data) will almost certainly yield a significant performance benefit of 10-25%. However, minor version differences (e.g., 8.1 vs 8.2) can produce variable results, making site-specific testing essential.
1.2 Server Efficiency: Doing More with Less
Beyond raw speed, PHP 8.x is fundamentally more efficient. It’;s engineered to use fewer server resources—namely CPU and memory—to accomplish the same tasks. This is a critical, though less visible, advantage.
When a visitor loads a page, your server executes PHP code to query the database, assemble the page structure, and render the final HTML. An inefficient process consumes more CPU cycles and allocates more RAM. On a high-traffic site, this can quickly lead to a bottleneck where the server becomes overwhelmed, causing slowdowns for everyone. High CPU usage is a common problem for growing WordPress sites, and upgrading PHP is one of the most effective first steps to mitigate it.
Sources like RoconPaas highlight that PHP 8.3 offers lower memory usage and better handling of concurrent traffic. This translates into direct, real-world benefits:
- Improved Scalability: Your server can handle more simultaneous visitors before performance starts to degrade. This is crucial for handling traffic spikes from marketing campaigns or viral content.
- Cost Savings: By running more efficiently, your site may be able to remain on a less expensive hosting plan for longer. You delay the need to upgrade your hardware, directly saving money.
- Enhanced Stability: A server that isn’t constantly hitting its resource limits is a more stable server. This reduces the risk of crashes, timeouts, and other resource-related errors.
Think of it as upgrading a car’s engine. A modern engine not only produces more horsepower (performance) but also has better fuel economy (efficiency). PHP 8.x gives your server both, allowing it to deliver a faster experience while consuming fewer resources.
1.3 SEO Impact: Climbing the Google Ranks
The performance gains from a PHP upgrade are not just a technical vanity metric; they are a powerful lever for improving your Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Google has been explicit for years that site speed is a ranking factor, and this has become even more critical with the introduction of Core Web Vitals.
Direct Impact on Core Web Vitals
Upgrading PHP directly and positively influences these key metrics:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): This measures how long it takes for a browser to receive the first byte of data from your server. A significant portion of TTFB is the server’s processing time. As Google’s research shows, user experience degrades rapidly with slow load times. By making PHP execution faster, you directly reduce TTFB.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): LCP measures how long it takes for the largest element on the page to become visible. A slow server response (high TTFB) delays everything that follows, including the rendering of the main content, thus worsening your LCP score. A faster PHP version gives the browser the data it needs sooner, leading to a better LCP.
Indirect SEO Benefits
The advantages extend beyond Core Web Vitals:
- Reduced Bounce Rate: The correlation between load time and bounce rate is undeniable. Google’s own data indicates that 53% of mobile users will abandon a page that takes longer than three seconds to load. A faster site keeps users engaged, sending positive user experience signals to Google.
- Improved Crawl Budget: Search engine bots have a finite amount of time and resources (a “crawl budget”) to dedicate to your site. A faster, more efficient server allows Googlebot to crawl more pages in a single session. This leads to better indexation coverage and faster discovery of new or updated content, which is a key aspect of technical SEO.
In the competitive landscape of 2025, where technical excellence is a baseline expectation, running on outdated PHP is a self-imposed handicap. SEO authorities like WPCrafter and Backlinko consistently list site speed and technical health as top-tier ranking factors. Upgrading your PHP version is one of the highest-impact, lowest-cost technical SEO improvements you can make.
1.4 The Security Imperative: A Non-Negotiable Upgrade
If the performance and SEO benefits aren’t compelling enough, the security implications should be. Using an old, unsupported version of PHP is a ticking time bomb. The open-source PHP project follows a predictable release cycle for each version: two years of active support (bug and security fixes) followed by one year of security fixes only. After that, the version reaches its “End-of-Life” (EOL) and receives no further updates of any kind.
This means that any new vulnerabilities discovered in an EOL version will remain unpatched forever, leaving your website as an easy target for hackers. As hosting providers like WP Engine state, for security purposes, they completely remove old versions of PHP from their servers once they reach EOL.
Here are the critical EOL dates to be aware of:
- PHP 7.4: Reached End-of-Life on November 28, 2022.
- PHP 8.0: Reached End-of-Life on November 26, 2023.
- PHP 8.1: Reached End-of-Life on November 25, 2024.
- PHP 8.2: Will receive security fixes only until December 8, 2025.
As of July 2025, any site running on PHP 8.1 or older is using a version that no longer receives active security support from the PHP community. Reputable hosting companies like Pressable have been actively migrating customers off these old versions, often automatically, because the risk is too great. While some companies offered extended support for a time, that grace period is long over. Staying on an EOL version is not a calculated risk; it’s a guarantee of future vulnerability.
Part 2: The “How-To”: Your Bulletproof PHP 8.x Upgrade Roadmap
Understanding the benefits is the first step. Now, we move to execution. The key to a successful PHP upgrade is not speed, but methodology. A rushed upgrade on a live site is a recipe for disaster. A careful, phased approach built on the principle of “Test, Test, and Test Again” virtually eliminates all risk. This section provides a comprehensive, three-phase roadmap to guide you through the process flawlessly.
Phase 1: Pre-Flight Checklist — Foundation for a Flawless Upgrade
Preparation is 90% of success. Before you even think about changing the PHP version, you must lay a solid foundation. Skipping these steps is the number one cause of upgrade-related problems. Treat this as a non-negotiable checklist.
| Category | Action Item | Recommended Tool/Method | Why It’s Critical |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Safeguarding | Full Website Backup (Files + Database) | Your host’s backup feature (e.g., Kinsta, WP Engine) or a trusted plugin like Duplicator. | This is your absolute safety net. If anything goes catastrophically wrong, a recent backup allows you to restore your site to its previous state in minutes. Always store a copy off-server. |
| 1. Safeguarding | Create a Staging Environment | Use your host’s one-click staging feature. Most quality managed WordPress hosts offer this. | The single most important step. A staging site is an exact clone of your live site in a private, sandboxed environment. This is where you will perform the upgrade and all testing without affecting your live site or its visitors. Never upgrade on a live site first. |
| 2. Housekeeping | Update WordPress Core | WordPress Dashboard > Updates | Ensures you have the latest version of WordPress, which includes the most recent compatibility fixes and security patches for modern PHP versions. WordPress.org officially recommends this. |
| 2. Housekeeping | Update All Themes & Plugins | WordPress Dashboard > Updates | This is the most common source of failure. Reputable developers regularly update their code to be compatible with new PHP versions. Running outdated plugins is a primary cause of fatal errors during an upgrade. |
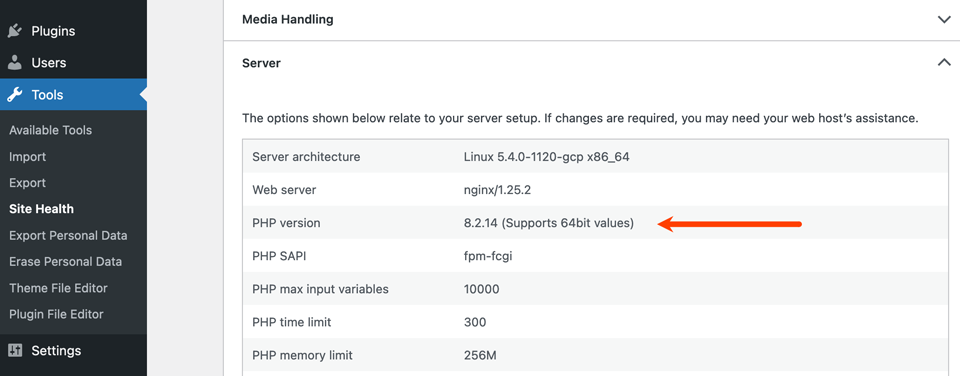
| 3. Compatibility | Check Host PHP Support | Hosting Control Panel (cPanel, MyKinsta, etc.) or the WordPress Site Health tool (Tools > Site Health > Info > Server). | Confirm that your hosting provider offers the target PHP version you want to use (e.g., 8.2, 8.3) and that all necessary PHP extensions (like mysqli, gd, curl) are enabled. |
| 3. Compatibility | Run Automated Compatibility Scan | The PHP Compatibility Checker plugin by WP Engine is a widely used tool. | This plugin scans your theme and plugin code against a set of rules for a specific PHP version. It will generate a report of potential warnings and errors, flagging code that uses deprecated functions or incorrect syntax. |
| 3. Compatibility | Review Scan Results | The plugin’s report page within your WordPress dashboard. | Carefully analyze the report. Make a list of all plugins and themes that show errors or warnings. Pay special attention to “abandoned” plugins that haven’t been updated in over a year, as they are unlikely to be fixed. |
| 3. Compatibility | Formulate a Plan for Incompatible Code | Research, documentation, and developer contact. | For each incompatible item identified, you must decide on a course of action: 1) Can it be replaced with a modern, well-maintained alternative? 2) Has the developer announced a fix or a beta version? 3) Do you need to hire a developer to patch the code? Do not proceed until you have a plan for every flagged item. |
Phase 2: Execution — The Two-Stage Upgrade Process
With your preparations complete, you’re ready to perform the upgrade. This is a methodical, two-stage process that ensures any and all issues are caught and resolved in the safety of your staging environment before the live site is ever touched.
Flowchart: The Safe PHP Upgrade Workflow
Full Website Backup (Files + Database)
Create Staging Environment (Clone of Live Site)
Change PHP version to 8.x in hosting panel for the staging site.
Enable WP_DEBUG and WP_DEBUG_LOG in wp-config.php.
Thoroughly test all front-end and back-end functionality. Check for visual glitches and functional errors.
Review /wp-content/debug.log for any Fatal Errors, Warnings, or Deprecated notices.
If errors are found, proceed to Fix. If not, the staging test is complete.
Isolate the problematic plugin/theme. Replace it, contact the developer, or patch the code. Then, return to Step 3 (TEST).
Schedule low-traffic window. Take final backup of live site.
Switch PHP version on the live production server.
Perform quick “smoke test” on live site. Monitor error logs and performance for 24-48 hours.
Upgrade complete.
Stage 1: On the Staging Site (The Sandbox)
Your staging site is your playground. Here, you can break things without any real-world consequences. This is where the real work happens.
- Switch the PHP Version: Navigate to your hosting provider’s control panel for your staging site. Locate the PHP version manager and change the version from its current setting (e.g., 7.4) to your target version (e.g., 8.3). This process is typically straightforward in modern hosting dashboards.
- Enable Debug Mode: This is a critical step for diagnostics. Connect to your staging site via FTP or your host’s File Manager. Open the
wp-config.phpfile and find the line that saysdefine( 'WP_DEBUG';, false );. Replace it with the following three lines. This will ensure that all errors are logged to a private file instead of being displayed publicly on the site, which can be a security risk.define( 'WP_DEBUG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false ); - Conduct Thorough Testing: This must be comprehensive. Don’t just glance at the homepage.
- Visual Check: Browse every major template of your site: homepage, single posts, pages, archive pages, contact page, etc. Look for the “White Screen of Death” (a completely blank page), broken layouts, missing images, or any visual glitches.
- Functional Check: Test every critical user workflow. Can users register or log in? Can they submit your contact forms? If you run an e-commerce site, can they add products to the cart, proceed to checkout, and complete a test transaction? In the backend, can you create, edit, and publish a new post? Can you upload media?
- Review the Debug Log: After testing, check the
/wp-content/debug.logfile. This file is your source of truth. Look for any entries, paying close attention to lines starting withPHP Fatal error,PHP Warning, andPHP Deprecated. A fatal error will break your site, while warnings and deprecation notices are signs of outdated code that should be addressed.
- Troubleshoot and Fix:If you encounter a fatal error or a broken feature, it’s almost certainly caused by a theme or plugin. Use the classic WordPress troubleshooting method:
- Deactivate all plugins.
- Switch to a default theme (like Twenty Twenty-Four).
- Check if the error is gone. If it is, you’ve confirmed the issue is in your theme or one of your plugins.
- Re-activate your theme. If the error returns, the theme is the problem.
- If the theme is fine, re-activate your plugins one by one, checking the site after each activation. The last plugin you activated before the error reappeared is the culprit.
Once you’ve identified the problematic component, refer to the plan you made in Phase 1. You may need to contact the developer, find a modern alternative, or hire a professional to patch the code. For example, many users on WordPress.org forums reported deprecation notices with the popular Contact Form 7 plugin when moving to PHP 8.1, which required a plugin update to resolve. These notices, while not fatal, indicate code that needs updating.
Repeat the testing and fixing cycle until your
debug.logis clean and all site functions work perfectly.
Stage 2: Going Live (The Production Environment)
Once your staging site is running perfectly on the new PHP version with no errors, you can be highly confident that your live site will too. The process for going live is now simple and low-risk.
- Schedule the Upgrade: Choose a time with the lowest traffic for your site, typically late at night or very early in the morning, to minimize any potential disruption.
- Take a Final Backup: Even with all the testing, perform one last full backup of your live site right before you make the switch. This is your final insurance policy.
- Switch the PHP Version: Log in to your live site’s hosting panel and confidently switch to the new PHP version that you have thoroughly tested.
- Perform a Smoke Test: Immediately after the switch, do a quick check of your live site. Load the homepage, a few key internal pages, and try logging into the WordPress admin area to ensure everything is operational.
Phase 3: Post-Launch Validation — Confirming Success
The job isn’t quite done when you flip the switch. For the next day or two, it’s wise to monitor the site to ensure everything is stable and performing as expected.
- [✔] Functional Sanity Check: Have a team member or a trusted user briefly re-run the most critical functional tests on the live site (e.g., complete a purchase, submit a form).
- [✔] Performance Monitoring: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to test your live site. Compare the new TTFB and load times to your pre-upgrade benchmarks. You should see a measurable improvement.
- [✔] Error Log Monitoring: Keep an eye on your server’s error logs (not the WordPress debug log, which should be disabled on a live site) for 24-48 hours. Your hosting provider’s dashboard should provide access to these. This will help you catch any rare, edge-case errors that didn’t appear during staging tests.
- [✔] SEO Monitoring: In the weeks following the upgrade, pay attention to your Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console. You should see a positive trend in your site’s performance scores.
Part 3: Advanced Tuning — Squeezing Out Every Drop of Performance
A standard PHP 8.x upgrade provides a fantastic baseline performance boost. However, for those looking to maximize speed, modern PHP works in concert with several server-side technologies. Understanding these allows you to go from “great” to “exceptional.”
3.1 OPcache: Your Server’s Short-Term Memory
What it is: OPcache is a bytecode caching engine built directly into PHP. When a PHP script (like a WordPress plugin file) is executed, it’s first compiled into a format the machine can understand, called bytecode. Without OPcache, this compilation happens every single time a page is loaded. OPcache stores this pre-compiled bytecode in fast server memory. On subsequent requests, PHP can skip the compilation step entirely, leading to a massive performance win.
Actionable Tip: Any quality WordPress host in 2025 will have OPcache enabled by default. You can verify it’;s active by checking your WordPress “Site Health”; tool. For high-traffic sites, the default settings may not be optimal. Advanced users can tune these settings in their php.ini file for even better performance. The configuration below, adapted from expert recommendations, is a solid starting point for a medium-to-large WordPress installation:
opcache.enable=1
opcache.memory_consumption=256 ; Allocate 256MB of memory
opcache.interned_strings_buffer=64 ; Memory for storing duplicated strings
opcache.max_accelerated_files=10000 ; Number of scripts to cache
opcache.revalidate_freq=0 ; Don't check for updates, rely on manual cache clearing
opcache.validate_timestamps=0 ; Improves performance by not checking file timestamps
opcache.fast_shutdown=1 ; Speeds up the process of shutting down PHP
Note: With settings like validate_timestamps=0, you must manually clear the OPcache after updating plugins, themes, or WordPress core for the changes to take effect. Most hosting panels provide a button for this.
3.2 JIT Compiler: A Nuanced Boost
What it is: The Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler, introduced in PHP 8.0, is a significant evolution of OPcache. While OPcache stores compiled bytecode, the JIT compiler can take things a step further. It identifies “hot” code paths—pieces of code that are executed very frequently—and compiles them all the way down to optimized machine code, which is even faster than bytecode. This brings PHP’s execution model closer to that of fully compiled languages like C++ for specific tasks.
The WordPress Reality: While JIT can produce dramatic speed-ups (2-3x or more) in CPU-intensive, mathematical, or long-running script scenarios, its impact on a typical WordPress site is more modest. WordPress is primarily an “I/O-bound” application, meaning its main performance bottlenecks are often waiting for the database (Input/Output) or external API calls, not raw CPU computation. Benchmarks from Wetopi show that for a standard WordPress request, the performance gain from JIT is often in the 3-8% range. It’s a welcome improvement, but it won’t magically fix a site slowed down by hundreds of bloated plugins or an unoptimized database.
Enabling JIT is generally beneficial, but it’s important to have realistic expectations. It’s the cherry on top, not the entire cake.
3.3 Object Caching: Tackling the Database Bottleneck
What it is: While OPcache and JIT optimize PHP execution, they do nothing to speed up your database. This is where object caching comes in. An object cache, powered by an in-memory data store like Redis or Memcached, stores the results of complex and frequently repeated database queries in the server’s RAM.
Why it Matters for WordPress: Many of WordPress’s performance issues stem not from slow PHP, but from slow or numerous database queries. Every time a page loads, WordPress might query the database for site options, widget configurations, navigation menus, and more. An object cache intercepts these requests. If the result is already in its memory, it returns it instantly without ever bothering the database. This dramatically reduces the load on your MySQL server and is especially impactful for:
- WooCommerce and Membership Sites: These sites have many logged-in users and generate dynamic, non-page-cacheable content. Object caching is essential for their performance.
- High-Traffic Blogs: Reduces the strain of generating pages for thousands of visitors.
- Snappier Admin Dashboard: Many backend operations are database-heavy. An object cache can make your WordPress admin area feel significantly faster.
For many complex WordPress sites, implementing a persistent object cache like Redis can provide a more significant real-world performance improvement than the JIT compiler alone, as it directly addresses the most common bottleneck.
Conclusion & Your Next Steps
Upgrading your WordPress site to PHP 8.x in 2025 is no longer just a “best practice”—it’s a strategic necessity for achieving optimal performance, robust security, and competitive SEO. The data is clear: a modern PHP version delivers a faster, more efficient, and more secure website. While the process can seem daunting, the risks are entirely manageable with a methodical approach.
By following the three-phase roadmap of Prepare, Execute, and Validate, you can navigate the upgrade with confidence. The key is to leverage a staging environment to test relentlessly, ensuring that any incompatibilities are discovered and resolved long before your live site is affected. The result is a seamless transition that unlocks significant speed gains, reduces server costs, and provides a superior experience for your users—an outcome that search engines like Google will reward.
Frequently Asked Questions (For “People Also Ask”)
Will upgrading PHP break my WordPress site?
It can if you do it blindly on a live site. However, if you follow our guide—especially by testing thoroughly on a staging environment first—the risk of breaking your site is extremely low. Incompatibility with an old plugin or theme is the most common issue, which you will identify and fix safely in the staging phase before your live site is ever touched.
Which PHP 8.x version is best for WordPress in 2025?
As of July 2025, PHP 8.3 is the recommended choice for most sites. It offers the best combination of performance improvements, new features, and is under active security support. Benchmarks generally show it as the fastest performer. PHP 8.2 is also a very stable and widely supported alternative if your host or a critical plugin does not yet fully support 8.3. Always check your host’s offerings and plugin compatibility.
What do I do if my favorite plugin or theme isn’t compatible with PHP 8.x?
First, check the developer’s website, plugin page, or support forums for an update or a compatibility statement. If none is available and the plugin hasn’t been updated in a long time, it’s a strong signal that you should find a modern, well-maintained alternative. An incompatible plugin is often a sign that it’s abandoned, which is a security risk in itself, regardless of the PHP version.
How much faster will my site be? Is it really noticeable?
Yes, in most cases, it is noticeable. Benchmarks consistently show that upgrading from PHP 7.4 to 8.3 can make your site handle 10-20% more requests per second and significantly reduce server response time (TTFB). For users, this translates to visibly faster page loads, a snappier admin dashboard, and a better overall experience, which is especially critical on e-commerce or high-traffic sites.

With over 27 years of hands-on SEO expertise, starting from my early days as a CFO. Quitting that job to build a top-ranked web hosting business in 1995, I’ve mastered WordPress optimization as a precise engineering discipline. Through extensive research, high-level consulting, and developing a WordPress site that achieved over a thousand organic Google rankings—culminating in a six-figure sale—I’ve decoded Google’s algorithm over 27 years to develop wordpress engineering that transforms underperforming WordPress sites into authoritative powerhouses. Business owners frustrated by stagnant traffic, low visibility, and missed opportunities find relief as I help them deliver measurable ROI through higher rankings, increased leads, and sustainable growth. As owner of dominant city-based SEO platforms in major U.S. markets, I outperform industry gurus, empowering entrepreneurs, local businesses, agencies, and marketers via my WordPress Optimization services at wordpressoptimization.com to unlock their site’s full potential.
